Difference between revisions of "Induction Motor Torque"
(Created page with "The torque developed in an induction machine can be calculated from the motor model / equivalent circuit because the torque developed is proportional...") |
|||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
:* [[Induction Motor Model]] | :* [[Induction Motor Model]] | ||
| − | :* [[Motor | + | :* [[Motor Driven Load]] |
[[Category:Modelling / Analysis]] | [[Category:Modelling / Analysis]] | ||
Revision as of 08:00, 22 November 2020
The torque developed in an induction machine can be calculated from the motor model / equivalent circuit because the torque developed is proportional to the square of rotor current, i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = \frac{pq}{4 \pi f} \frac{R_{r}}{s} I_{r}^{2} \, }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T \, } is the torque developed in the motor (N-m)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p \, } is the number of motor poles
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q \, } is the number of stator phases
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f \, } is the nominal frequency (Hz)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{r} \, } is the equivalent rotor resistance ()
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s \, } is the motor slip (pu)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{r} \, } is the rotor current (A)
Calculating Per-Unit Torque from the Equivalent Circuit
By using per unit values, the constant terms can be eliminated and the equation above reduces to:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = \frac{R_{r}}{s} I_{r}^{2} \, }
Where in this equation, all quantities are in per-unit.
Using this relationship, we can simply analyse the equivalent circuit of an induction motor and solve for the rotor current. For simplicity, all of the analyses below will be performed using per unit values. Note also that complex impedances (or admittances) obey the rules of complex arithmetic.
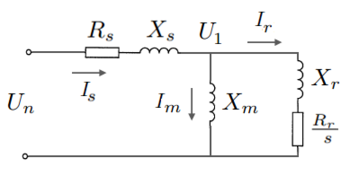
Single Cage Model
The equivalent circuit for the single cage model is shown in the figure to the right. Recasting the impedances as admittances:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{s} = \frac{1}{R_{s} + j X_{s}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{m} = \frac{1}{j X_{m}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{r1} = \frac{1}{\frac{R_{r}}{s} + j X_{r}} \, }
Applying Kirchhoff's law at node Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{1} \,} :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left( U_{n} - U_{1} \right) Y_{s} = U_{1} \left( Y_{m} + Y_{r} \right) \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{1} = \frac{U_{n} Y_{s}}{Y_{s} + Y_{m} + Y_{r}} \, }
The per-unit stator current Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{s} \,} :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{s} = \left( U_{n} - U_{1} \right) Y_{s} \,}
The per-unit rotor current Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{r} \,} :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{r} = U_{1} Y_{r} \,}
The per-unit torque developed is:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = \frac{R_{r}}{s} I_{r}^{2} \,}
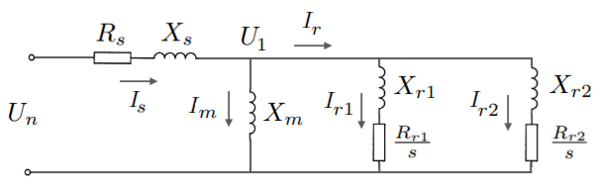
Double Cage Model
The equivalent circuit for the double cage model is shown in the figure to the right. Recasting the impedances as admittances:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{s} = \frac{1}{R_{s} + j X_{s}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{m} = \frac{1}{j X_{m}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{r1} = \frac{1}{\frac{R_{r1}}{s} + j X_{r1}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{r2} = \frac{1}{\frac{R_{r2}}{s} + j X_{r2}} \, }
Applying Kirchhoff's law at node Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{1} \,} :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left( U_{n} - U_{1} \right) Y_{s} = U_{1} \left( Y_{m} + Y_{r1} + Y_{r2} \right) \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{n} Y_{s} = U_{1} \left( Y_{s} + Y_{m} + Y_{r1} + Y_{r2} \right) \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{1} = \frac{U_{n} Y_{s}}{Y_{s} + Y_{m} + Y_{r1} + Y_{r2}} \, }
The per-unit stator current Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{s} \,} :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{s} = \left( U_{n} - U_{1} \right) Y_{s} \,}
The per-unit rotor currents Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{r1} \,} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{r2} \,} :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{r1} = U_{1} Y_{r1} \,}
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{r2} = U_{1} Y_{r2} \,}
The per-unit torque developed is:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = \frac{R_{r1}}{s} I_{r1}^{2} + \frac{R_{r2}}{s} I_{r2}^{2} \,}
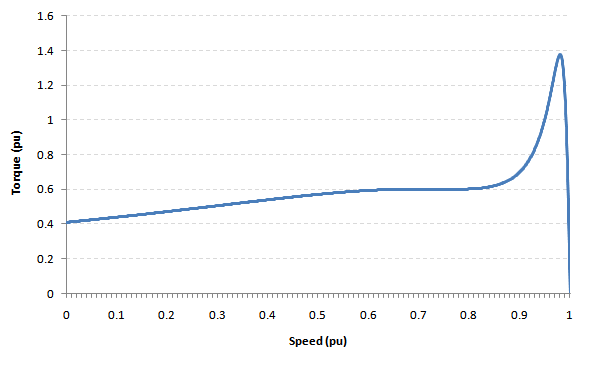
Torque-Speed Curves
Based on the torque equations developed in the previous section for the single cage and double cage motor models, torque-speed curves can be constructed from the equivalent circuit by calculating the torque at each point on the full range of motor speeds (i.e. from standtill to synchronous speed).