Frequency Dependent Line Model
Motivation
In this section, we try to answer the question - why bother with a model for frequency dependent lines?
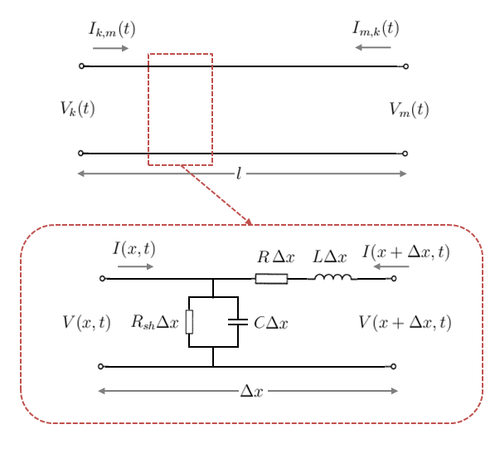
Consider the generic single-phase distributed parameter line model of length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l \,} metres shown in Figure 1. Note that the model is represented as functions of both distance and time.
We can represent the series elements as an impedance and the shunt elements as an admittance as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{z} = R + j \omega L = R + jX \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{y} = \frac{1}{R_{sh}} + j \omega C = G + jB \, }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R \, } is the series resistance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega /m } )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X \, } is the series reactance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega /m } )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G \, } is the shunt conductance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S /m } )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B \, } is the shunt susceptance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S /m } )
If we only consider this model in the steady-state (i.e. the frequency domain), then time can be neglected and the model is exactly like the conventional single-phase distributed parameter line model.
Recall that the solution to the voltage and current of the steady-state model is as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}_{k} = \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{m} - \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \right) e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} + \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{m} + \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \right) e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} \, } ... Equ. (1)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}_{k,m} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{m} - \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \right) e^{\gamma l} - \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{m} + \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \right) e^{-\gamma l} \, } ... Equ. (2)
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\gamma} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{zy}} = \sqrt{(R + j \omega L)(G + j \omega C)} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{\frac{z}{y}}} = \sqrt{\frac{(R + j \omega L)}{(G + j \omega C)}} }
Things to note:
- 1) Voltage and current are complex phasors hence they are in bold.
- 2) The equations have slightly different signs to those derived in the distributed parameter line model. This is because the direction of current Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I_{m,k}(t) \, } in Figure 3 is set in the opposite direction in this model.
We can add Equ. (1) to Equ. (2) to get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}_{k} + \boldsymbol{I}_{k,m} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \left( \boldsymbol{V}_{m} - \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \right) e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} \, } ... Equ. (3)
Similarly, we can subtract Equ. (2) from Equ. (1) to get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}_{k} - \boldsymbol{I}_{k,m} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \left( \boldsymbol{V}_{m} + \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \right) e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} \, } ... Equ. (4)
Re-arranging Equ. (3) and Equ. (4) to solve for the currents Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} \, }
and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}_{k,m} \, }
:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} = \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{m}}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} - \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{k}}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} - \boldsymbol{I}_{k,m} e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} \, } ... Equ. (5)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}_{k,m} = \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{k}}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} - \frac{\boldsymbol{V}_{m}}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} - \boldsymbol{I}_{m,k} e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} \, } ... Equ. (6)
From Fourier Transform theory, we know that multiplying by a complex exponential in the frequency domain is equivalent to a time shift in the time domain. Therefore, in the lossless case (i.e. R = G = 0.), the exponential part of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} \, } is:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\gamma} l = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{zy}} l = \sqrt{(j \omega L)(j \omega C)} l = j \omega \sqrt{LC} l = j \omega \tau }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau \, } is the travel time that we saw in the Bergeron model.
The characteristic impedance is also a scalar frequency-independent constant:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{\frac{z}{y}}} = \sqrt{\frac{(j \omega L)}{(j \omega C)}} = \sqrt{\frac{L}{C}}}
However if the line is not lossless, then we can see that the propagation constant and characteristic impedance are frequency dependent, i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\gamma} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{zy}} = \sqrt{(R + j \omega L)(G + j \omega C)} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{\frac{z}{y}}} = \sqrt{\frac{(R + j \omega L)}{(G + j \omega C)}} }
Since these quantities are complex and frequency dependent, the model does not simplify to a simple time shift in the time domain as we saw in the lossless case.
Moreover, the line parameters themselves are frequency dependent rather than constant across the full frequency range, i.e. Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle L(\omega) \, } , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C(\omega) \, } , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R(\omega) \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G(\omega) \, } . Therefore, a constant parameter line model such as the Bergeron model is not suitable for cases where the frequency dependencies are significant (e.g. zero sequence impedances). This is the motivation for developing models that are able to capture the frequency dependencies of lines.