Difference between revisions of "Induction Motor Performance"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
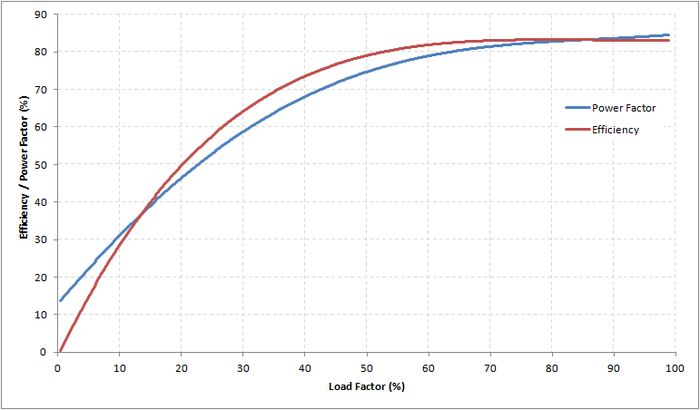
| − | Induction motors typically run at highest efficiency and power factor at full-load. However when motors are run at lower | + | Induction motors typically run at highest efficiency and power factor at full-load. However when motors are run at lower operating points, there is generally a corresponding decline in performance. This drop in performance tends to vary non-linearly (with respect to the load factor), with larger drops in performance at low load factors (0% to 40%). For example, the figure below shows the performance test data of a 155kW, 2000V, 50Hz induction motor at load factors from 0% to 100%: |
[[Image:Motor_performance.png|700px]] | [[Image:Motor_performance.png|700px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:35, 22 November 2020
Induction motors typically run at highest efficiency and power factor at full-load. However when motors are run at lower operating points, there is generally a corresponding decline in performance. This drop in performance tends to vary non-linearly (with respect to the load factor), with larger drops in performance at low load factors (0% to 40%). For example, the figure below shows the performance test data of a 155kW, 2000V, 50Hz induction motor at load factors from 0% to 100%: