Distributed Parameter Line Model
This article describes the steady-state or frequency domain distributed parameter line model. By steady-state, we mean that the voltage and current along the line are steady and do not change with time.
Single-Phase Distributed Parameter Model
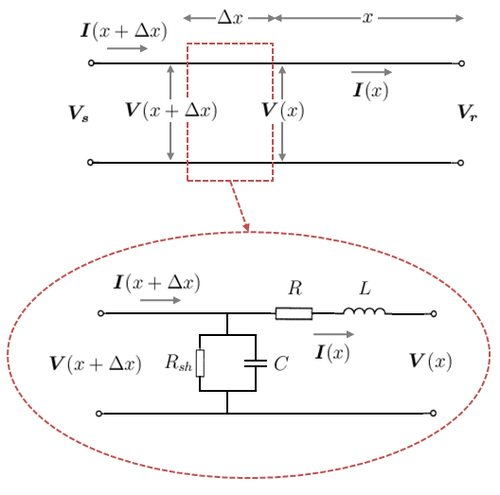
In a real transmission line, the R, L and C circuit elements are not lumped together, but are uniformly distributed along the length of the line. In order to capture the distributed nature of the circuit parameters, consider the single-phase line model in Figure 1. In particular, consider a small line segment of length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta x } metres, which is located at a distance Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} metres from the receiving end bus.
The top diagram of Figure 1 shows the complete transmission line and the small line segment is represented by the dotted box. The bottom diagram is an expanded view of the line segment showing a typical line segment model with series and shunt circuit elements. The series elements can be represented as an impedance and the shunt elements can be represented as an admittance as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{z} = R + j \omega L = R + jX \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{y} = \frac{1}{R_{sh}} + j \omega C = G + jB \, }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R \, } is the series resistance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega /m } )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X \, } is the series reactance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega /m } )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G \, } is the shunt conductance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S /m } )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B \, } is the shunt susceptance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S /m } )
Note that the impedance and admittance are denoted in per-length values (i.e. per metre). Therefore, the series impedance of a line segment of length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta x } metres is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{z} \Delta x \, } . The same logic applies for the shunt admittance.
Derivation of Voltage and Current Equations
Analysing this circuit using Kirchhoff's voltage law:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(x + \Delta x) = \boldsymbol{V}(x) + \boldsymbol{z} \Delta x \boldsymbol{I}(x) \, }
Re-arranging this equation, we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\boldsymbol{V}(x + \Delta x) - \boldsymbol{V}(x)}{\Delta x} = \boldsymbol{z} \boldsymbol{I}(x) \, }
The left-hand side is Newton's difference quotient and the limit as Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta x \to 0} is by definition the derivative of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(x)} , i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lim_{\Delta x \to 0} \frac{\boldsymbol{V}(x + \Delta x) - \boldsymbol{V}(x)}{\Delta x} = \frac{d \boldsymbol{V}(x)}{dx} = \boldsymbol{z} \boldsymbol{I}(x) \, } ... Equ. (1)
Similarly, analysing the circuit using Kirchhoff's current law:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}(x + \Delta x) = \boldsymbol{I}(x) + \boldsymbol{y} \Delta x \boldsymbol{V}(x + \Delta x) \, }
Re-arranging this equation, we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\boldsymbol{I}(x + \Delta x) - \boldsymbol{I}(x)}{\Delta x} = \boldsymbol{y} \boldsymbol{V}(x + \Delta x) \, }
Taking the limit of both sides as Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta x \to 0} :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d \boldsymbol{I}(x)}{dx} = \boldsymbol{y} \boldsymbol{V}(x) \, } ... Equ. (2)
Differentiating Equations (1) and (2) again with respect to Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x }
, we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V}(x)}{dx^{2}} = \boldsymbol{z} \frac{d \boldsymbol{I}(x)}{dx} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I}(x)}{dx^{2}} = \boldsymbol{y} \frac{d \boldsymbol{V}(x)}{dx} \, }
We can re-substitute Equations (1) and (2) into the above to get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V}(x)}{dx^{2}} = \boldsymbol{zy} \boldsymbol{V}(x) \, } ... Equ. (3)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I}(x)}{dx^{2}} = \boldsymbol{zy} \boldsymbol{I}(x) \, } ... Equ. (4)
The pair of equations above can be re-arranged to form homogenous second-order linear ordinary differential equations, i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V}(x)}{dx^{2}} - \boldsymbol{zy} \boldsymbol{V}(x) = 0 \, }
The general solution to this differential equation is:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(x) = A_{1} e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} + A_{2} e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} \, }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\gamma} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{zy}} } is known as the propagation constant (with units Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{-1}} )
Plugging this solution back into Equ. (1), we can also solve for Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}(x)} , i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx} \left[ A_{1} e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} + A_{2} e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} \right] = \boldsymbol{z} \boldsymbol{I}(x) \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow \boldsymbol{I}(x) = \frac{A_{1} e^{\gamma x} - A_{2} e^{-\gamma x}}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} \, }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{\frac{z}{y}}} } is known as the characteristic impedance or surge impedance (with units Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega} )
We can solve for the constants Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_{1} \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_{2} \, } by using the boundary conditions at the receiving end of the line, i.e. at the receiving end, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x = 0 \, } , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(0) = \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}(0) = \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, } . The solution is as follows (see the full derivation here):
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_{1} = \frac{\boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_{2} = \frac{\boldsymbol{V_{r}} - \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \, }
Substituting these constants, we get the final distributed parameter transmission line equations:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(x) = \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \right) e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} + \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V_{r}} - \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2} \right) e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} \, } ... Equ. (5)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}(x) = \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2 \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} \right) e^{\gamma x} - \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{V_{r}} - \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}}{2 \boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} \right) e^{-\gamma x} \, } ... Equ. (6)
Hyperbolic Form of Transmission Line Equations
Equations (5) and (6) can be re-arranged as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(x) = \left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} + e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} x}}{2} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} - e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} x}}{2} \right) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}(x) = \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} \left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} - e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} x}}{2} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol{\gamma} x} + e^{-\boldsymbol{\gamma} x}}{2} \right) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} }
Given the exponential forms of the hyperbolic functions Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sinh x } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \cosh x } :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sinh x = \frac{e^{x} - e^{-x}}{2} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \cosh x = \frac{e^{x} + e^{-x}}{2} }
We can substitute these into the transmission line equations to get the well-known hyperbolic form of the equations:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(x) = \cosh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \sinh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}(x) = \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} \sinh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \cosh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} }
For a line of length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l \, } metres, the ABCD parameters of the above equations can be represented in matrix form as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \cosh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) & \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \sinh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) \\ \\ \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} sinh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) & \cosh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
where the sending end quantities are Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} = \boldsymbol{V}(l) \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{s}} = \boldsymbol{I}(l) \, }
Multi-conductor Distributed Parameter Model
The distributed parameter model can be extended to a multi-conductor line of n conductors by replacing the voltage and current phasors with Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n \times 1 } vectors, e.g. for a three-phase, three-conductor line:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V} = \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{a}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{b}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{c}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, } , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I} = \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{a}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{b}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{c}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, }
And the impedance and admittance with Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n \times n } complex matrices, e.g. for a three-phase, three-conductor line:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z] = \left[ \begin{matrix} Z_{aa} & Z_{ab} & Z_{ac} \\ Z_{ba} & Z_{bb} & Z_{bc} \\ Z_{ca} & Z_{cb} & Z_{cc} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Y] = \left[ \begin{matrix} Y_{aa} & Y_{ab} & Y_{ac} \\ Y_{ba} & Y_{bb} & Y_{bc} \\ Y_{ca} & Y_{cb} & Y_{cc} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
Equations (1) and (2) above in the single-phase model can now be re-written in the multi-conductor model as:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d \boldsymbol{V}}{dx} = [Z] \boldsymbol{I} \, } ... Equ. (7)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d \boldsymbol{I}}{dx} = [Y] \boldsymbol{V} \, } ... Equ. (8)
Differentiating these equations with respect to Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x } , we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V}}{dx^{2}} = [Z] \frac{d \boldsymbol{I}}{d x} \, } ... Equ. (9)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I}}{dx^{2}} = [Y] \frac{d \boldsymbol{V}}{d x} \, } ... Equ. (10)
Substituting Equ. (8) into Equ. (9) and Equ. (7) into Equ. (10), we end up with the multi-conductor equivalent of equations (3) and (4):
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V}}{dx^{2}} = [Z] [Y] \boldsymbol{V} \, } ... Equ. (11)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I}}{dx^{2}} = [Y] [Z] \boldsymbol{I} \, } ... Equ. (12)
The issue with the multi-conductor case is that because the matrices [Z] and [Y] are full, then their product [Z][Y] or [Y][Z] is also full. For example, if we were to expand out Equ. (11):
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V_{a}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V_{b}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2}\boldsymbol{V_{c}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} Z_{aa} & Z_{ab} & Z_{ac} \\ Z_{ba} & Z_{bb} & Z_{bc} \\ Z_{ca} & Z_{cb} & Z_{cc} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} Y_{aa} & Y_{ab} & Y_{ac} \\ Y_{ba} & Y_{bb} & Y_{bc} \\ Y_{ca} & Y_{cb} & Y_{cc} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{a}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{b}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{c}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, }
The first line of the system of equations above can be expanded as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V_{a}}(x)}{dx^{2}} = \left( Z_{aa}Y_{aa} + Z_{ab}Y_{ba} + Z_{ac}Y_{ca} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{a}}(x) + \left( Z_{aa}Y_{ab} + Z_{ab}Y_{bb} + Z_{ac}Y_{cb} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{b}}(x) + \left( Z_{aa}Y_{ac} + Z_{ab}Y_{bc} + Z_{ac}Y_{cc} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{c}}(x) \, }
Unlike in the single-phase case above, there is no closed-form general solution to this second-order differential equation (because of the cross-coupling between phases). The so-called modal transformation is required to decouple the phases from equations (11) and (12).
Modal Transformation
The modal transformation is a technique for decoupling the phases from equations (11) and (12) based on an Eigenvalue decomposition. In this section, we will develop the modal transformation from first principles. Alternative derivations can be found in [1], [2] and [3].
Consider linear transforms of the voltage and current vectors denoted Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V'}} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I'}} , where by convention, the subscripts change from phases (abc) to modes (012), i.e. for a three-phase, three-conductor line:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V'} = \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, } , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I'} = \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, }
Suppose that the original quantities are related to the transformed quantities as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V} = [T_{v}] \boldsymbol{V'}} ... Equ. (13)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I} = [T_{i}] \boldsymbol{I'}} ... Equ. (14)
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{v}] \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{i}] \, } are Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n \times n } transformation matrices. We won't define the transformation matrices just yet, but it will become obvious later on that they are actually the eigenvectors of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z][Y] \,} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Y][Z] \,} respectively.
Substituting these transformed quantities into equations (7) and (8):
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d [T_{v}] \boldsymbol{V'}}{dx} = [Z] [T_{i}] \boldsymbol{I'} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d [T_{i}] \boldsymbol{I'}}{dx} = [Y] [T_{v}] \boldsymbol{V'} \, }
Supposing that the transformation matrices Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{v}] \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{i}] \, } are independent of x, we can re-arrange the equations above as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d \boldsymbol{V'}}{dx} = [T_{v}]^{-1} [Z] [T_{i}] \boldsymbol{I'} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d \boldsymbol{I'}}{dx} = [T_{i}]^{-1} [Y] [T_{v}] \boldsymbol{V'} \, }
Following the same procedure as before, i.e. differentiating the equations by x and substituting, we end up with:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V'}}{dx^{2}} = [T_{v}]^{-1} [Z] [Y] [T_{v}] \boldsymbol{V'} \, } ... Equ. (15)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I'}}{dx^{2}} = [T_{i}]^{-1} [Y] [Z] [T_{i}] \boldsymbol{I'} \, } ... Equ. (16)
In order for us to decouple the phases in equations (15) and (16), we need Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{v}]^{-1} [Z] [Y] [T_{v}] \,} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{i}]^{-1} [Y] [Z] [T_{i}] \,} to be diagonal matrices, i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle diag(\boldsymbol{\lambda_{v}}) = [T_{v}]^{-1} [Z] [Y] [T_{v}] \,}
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle diag(\boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}) = [T_{i}]^{-1} [Y] [Z] [T_{i}] \,}
It is apparent from inspection that the transformation matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{v}] \, } and diagonal matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle diag(\boldsymbol{\lambda_{v}}) } are the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z][Y] \,} respectively.
Similarly, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [T_{i}] \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle diag(\boldsymbol{\lambda_{v}}) } are the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Y][Z] \,} .
Furthermore, since the matrices Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z] \,} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Y] \,} are both symmetric, then Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z][Y] = \left( [Y][Z] \right)^{T} \,} . We know that the eigenvalues of a matrix and its transpose are the same, so therefore Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z][Y] \,} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Y][Z] \,} also share the same eigenvalues, i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle diag(\boldsymbol{\lambda_{v}}) = diag(\boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}) = diag(\boldsymbol{\lambda})\,}
We can now re-write equations (15) and (16) as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2}\boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \lambda_{0} & & \\ & \lambda_{1} & \\ & & \lambda_{2} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (17)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2}\boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \lambda_{0} & & \\ & \lambda_{1} & \\ & & \lambda_{2} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (18)
Recall from the single-phase case that the propagation constant is defined as Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\gamma} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{zy}} } . In multi-conductor matrix form, this can be written as a propagation matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\Gamma] \, } as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\Gamma] = ([Z][Y])^{\frac{1}{2}} \, }
Let the eigenvalues of the propagation matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\Gamma] \, } be Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \gamma_0, \gamma_1, \gamma_2 \, } .
A property of eigenvalues is that if matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A \, } has the eigenvalues Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_1, \lambda_2, ... , \lambda_n \,} , then matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A^{k} \, } has the eigenvalues Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_1^{k}, \lambda_2^{k}, ... , \lambda_n^{k} \,} .
Therefore, since Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_0, \lambda_1, \lambda_2 \, } are the eigenvalues of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z][Y] \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \gamma_0, \gamma_1, \gamma_2 \, } are the eigenvalues of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ([Z][Y])^{\frac{1}{2}} \, } , we can say that:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \lambda_{0} & & \\ & \lambda_{1} & \\ & & \lambda_{2} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \gamma_{0}^{2} & & \\ & \gamma_{1}^{2} & \\ & & \gamma_{2}^{2} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
We can now re-write equations (17) and (18) as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2}\boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \gamma_{0}^{2} & & \\ & \gamma_{1}^{2} & \\ & & \gamma_{2}^{2} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (19)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2} \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \\ \\ \frac{d^{2}\boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x)}{dx^{2}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \gamma_{0}^{2} & & \\ & \gamma_{1}^{2} & \\ & & \gamma_{2}^{2} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (20)
Each of these decoupled modal differential equations above can now be solved using the general solution:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x) = A_{0} e^{\gamma_0 x} + B_{0} e^{-\gamma_0 x} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x) = A_{1} e^{\gamma_1 x} + B_{1} e^{-\gamma_1 x} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x) = A_{2} e^{\gamma_2 x} + B_{2} e^{-\gamma_2 x} \, }
Taking the first derivative of the equations above with respect to x, we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{d \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x)}{dx} \\ \\ \frac{d \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x)}{dx} \\ \\ \frac{d\boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x)}{dx} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \gamma_{0} & & \\ & \gamma_{1} & \\ & & \gamma_{2} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} A_{0} e^{\gamma_0 x} - B_{0} e^{-\gamma_0 x}\\ A_{1} e^{\gamma_1 x} - B_{1} e^{-\gamma_1 x} \\ A_{2} e^{\gamma_2 x} - B_{2} e^{-\gamma_2 x} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (21)
Let's denote equation (21) above in the following shorthand notation:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d\boldsymbol{V'}}{dx} = [\gamma] \boldsymbol{V_x} \, } ... Equ. (22)
Recall from earlier that:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d \boldsymbol{V'}}{dx} = [T_{v}]^{-1} [Z] [T_{i}] \boldsymbol{I'} \, }
Equating this with equation (22) and solving for Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_x} } , we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_x} = [\gamma]^{-1} [T_{v}]^{-1} [Z] [T_{i}] \boldsymbol{I'} \, }
We define the modal characteristic impedance matrix (or modal surge impedance matrix) as:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z_c] = [\gamma]^{-1} [T_{v}]^{-1} [Z] [T_{i}] \, } ... Equ. (23)
Using this definition, the modal current vector can be expressed as:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I'} = [Z_c]^{-1} \boldsymbol{V_x} \, } ... Equ. (24)
It can be shown that if Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\gamma] \, } is diagonal, then Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [Z_c] \, } is also diagonal (see the derivation here). Therefore, when expanded, equation (24) looks like this:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_0}} & & \\ & \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_1}} & \\ & & \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_2}} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} A_{0} e^{\gamma_0 x} - B_{0} e^{-\gamma_0 x}\\ A_{1} e^{\gamma_1 x} - B_{1} e^{-\gamma_1 x} \\ A_{2} e^{\gamma_2 x} - B_{2} e^{-\gamma_2 x} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (25)
Boundary Conditions
We now have the following six modal equations that we can solve using boundary conditions:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} A_{0} e^{\gamma_0 x} + B_{0} e^{-\gamma_0 x} \\ A_{1} e^{\gamma_1 x} + B_{1} e^{-\gamma_1 x} \\ A_{2} e^{\gamma_2 x} + B_{2} e^{-\gamma_2 x} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_0}} & & \\ & \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_1}} & \\ & & \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_2}} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} A_{0} e^{\gamma_0 x} - B_{0} e^{-\gamma_0 x}\\ A_{1} e^{\gamma_1 x} - B_{1} e^{-\gamma_1 x} \\ A_{2} e^{\gamma_2 x} - B_{2} e^{-\gamma_2 x} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
The boundary conditions at the receiving end Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_r} } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_r} } must be transformed to modal quantities as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_r}' = [T_v]^{-1} \boldsymbol{V_r} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_r}' = [T_i]^{-1} \boldsymbol{I_r} }
At the receiving end (i.e. x = 0), the modal equations reduce as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} A_{0} + B_{0} \\ A_{1} + B_{1} \\ A_{2} + B_{2} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{Z_0} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{Z_1} \boldsymbol{I_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{Z_2} \boldsymbol{I_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} A_{0} - B_{0} \\ A_{1} - B_{1} \\ A_{2} - B_{2} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
Solving for the constants of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [A] \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [B] \, } :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} A_{0} \\ A_{1} \\ A_{2} \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{2} \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_0} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_1} \boldsymbol{I_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_2} \boldsymbol{I_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (26)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} B_{0} \\ B_{1} \\ B_{2} \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{2} \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_0} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_1} \boldsymbol{I_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_2} \boldsymbol{I_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (27)
These constants can be plugged back into the modal voltage and current equations to get the final expressions:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{2} \left[ \begin{matrix} (\boldsymbol{V_{0r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_0} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}}) e^{\gamma_0 x} + (\boldsymbol{V_{0r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_0} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}}) e^{-\gamma_0 x} \\ (\boldsymbol{V_{1r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_1} \boldsymbol{I_{1r}}) e^{\gamma_1 x} + (\boldsymbol{V_{1r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_1} \boldsymbol{I_{1r}}) e^{-\gamma_1 x} \\ (\boldsymbol{V_{2r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_2} \boldsymbol{I_{2r}}) e^{\gamma_2 x} + (\boldsymbol{V_{2r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_2} \boldsymbol{I_{2r}}) e^{-\gamma_2 x} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (28)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{1}{2 \boldsymbol{Z_0}} & & \\ & \frac{1}{2 \boldsymbol{Z_1}} & \\ & & \frac{1}{2 \boldsymbol{Z_2}} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} (\boldsymbol{V_{0r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_0} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}}) e^{\gamma_0 x} - (\boldsymbol{V_{0r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_0} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}}) e^{-\gamma_0 x} \\ (\boldsymbol{V_{1r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_1} \boldsymbol{I_{1r}}) e^{\gamma_1 x} - (\boldsymbol{V_{1r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_1} \boldsymbol{I_{1r}}) e^{-\gamma_1 x} \\ (\boldsymbol{V_{2r}} - \boldsymbol{Z_2} \boldsymbol{I_{2r}}) e^{\gamma_2 x} - (\boldsymbol{V_{2r}} + \boldsymbol{Z_2} \boldsymbol{I_{2r}}) e^{-\gamma_2 x} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (29)
Hyperbolic Form of Multi-conductor Line Equations
As in the single-phase distributed parameter model, the final modal voltages and currents shown in equations (28) and (29) can be converted to the following hyperbolic forms:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \cosh{(\gamma_0 x)} & & \\ & \cosh{(\gamma_1 x)} & \\ & & \cosh{(\gamma_2 x)}\end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] + \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{Z_0} \sinh{(\gamma_0 x)} & & \\ & \boldsymbol{Z_1} \sinh{(\gamma_1 x)} & \\ & & \boldsymbol{Z_2} \sinh{(\gamma_2 x)} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (30)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1}}(x) \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2}}(x) \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_0}} \sinh{(\gamma_0 x)} & & \\ & \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_1}} \sinh{(\gamma_1 x)} & \\ & & \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z_2}} \sinh{(\gamma_2 x)}\end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{V_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] + \left[ \begin{matrix} \cosh{(\gamma_0 x)} & & \\ & \cosh{(\gamma_1 x)} & \\ & & \cosh{(\gamma_2 x)} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{I_{0r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{1r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{2r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, } ... Equ. (31)
Derivations of these forms are straightforward and left to the interested reader to prove.
References
- [1] Wedepohl, L. M., "Application of matrix methods to the solution of travelling-wave phenomena in polyphase systems", Proceedings of the IEE, Vol. 110(12), 1963
- [2] Hedman, D. E., "Propagation on Overhead Transmission Lines I - Theory of Modal Analysis ", IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, Vol 84(3), 1965
- [3] Bowman, W. I., and McNamee, J. M., "Development of Equivalent Pi and T Matrix Circuits for Long Untransposed Transmission Lines", IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, Vol 83(6), 1964