Single-Phase Line Models
ABCD Parameters (Generalised Line Constants)
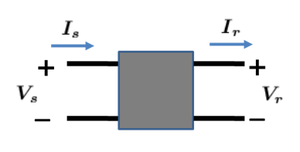
Consider the overhead line represented as a two-port network of the form:
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \, } is the voltage at the sending end
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \, } is the voltage at the receiving end
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \, } is the current at the sending end
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, } is the current at the receiving end
Suppose the system can be represented such that the sending end quantities can be written as a linear function of the receiving end quantities, i.e.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} = A \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + B \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{s}} = C \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + D \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
Where that the parameters Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A \, } , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B \, } , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C \, } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D \, } are constants (which can be either real or complex). These constants are called the ABCD parameters of the line. Sometimes, they are referred to as Generalised Line Constants.
In matrix form, the ABCD parameters are represented as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} A & C \\ B & D \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
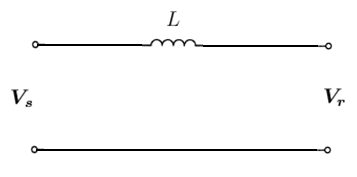
Lossless (L) Line
In its simplest form, we neglect the line resistance and capacitance and represent the line as purely inductive, i.e. the line impedance Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z} = j \omega L = X_{L} \, } .
Analysing this circuit using Kirchhoff's laws, we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} = \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + X_{L} \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{s}} = \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
Therefore the ABCD parameters of the lossless (L) line in matrix form are:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & X_{L} \\ 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
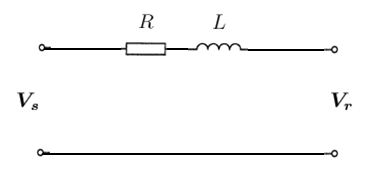
RL Line
The lossless (L) line model can be made more realistic by adding a resistive component, i.e. Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z} = R + j \omega L \, } .
Using the same logic as the lossless (L) line above, the sending end quantities can be calculated as:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} = \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{s}} = \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
Therefore the ABCD parameters of the RL line in matrix form are:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & \boldsymbol{Z} \\ 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
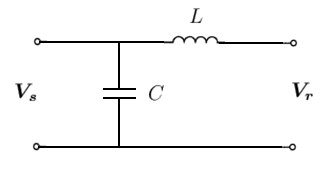
Lossless (LC) Line
We've so far neglected capacitances in our line, but at higher voltages and longer line lengths, the effect of shunt capacitances becomes more significant. So we now consider a lossless LC line of the form:
The inductance and capacitance can be represented as a reactance and susceptance as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X_{L} = j \omega L \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{C} = j \omega C \, }
Analysing this circuit using Kirchhoff's laws, we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} = \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + X_{L} \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{s}} = Y_{C} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} + \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = Y_{C} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \left( 1 + X_{L} Y_{C} \right) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
Therefore the ABCD parameters of the LC line in matrix form are:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & X_{L} \\ Y_{C} & 1 + X_{L} Y_{C} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \\ \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
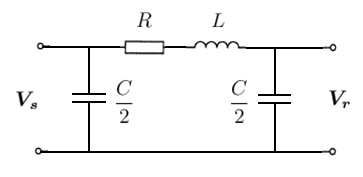
Nominal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} Line
The so-called "Nominal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} " model is an extension of the lossless LC line where a series resistance is added and the shunt capacitances are balanced (i.e. half at each end of the line).
The series elements can be represented as an impedance and the shunt capacitances as susceptances as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z} = R + j \omega L \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} = j \omega \left( \frac{C}{2} \right) \, }
Before we analyse the circuit, it is worth noting from Kirchhoff's current law that the current across the series impedance Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z} } is:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{z}} = \boldsymbol{I_{r}} + \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \, }
Analysing this circuit using Kirchhoff's laws, we get:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} = \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{I_{z}} \, }
Substituting in Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{z}} } :
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V_{s}} = \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z} \left( \boldsymbol{I_{r}} + \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \right) \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I_{s}} = \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} + \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \left[ \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \right] + \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \boldsymbol{Y} \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{Y}}{4} \right) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \right) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \, }
Therefore the ABCD parameters of the nominal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} line in matrix form are:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \right) & \boldsymbol{Z} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{Y} \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{Y}}{4} \right) & \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z} \boldsymbol{Y}}{2} \right) \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
Distributed Parameter Line
Refer to the distributed parameter model article for the detailed derivation of the model.
The models above have been "lumped", such that the line has been represented by lumped R, L and C elements. However in reality, the R, L and C elements are distributed along the length of the line. So now let's consider a distributed parameter model where the voltage and current at any point Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x \, } along the line (relative to the receiving end bus) are given by the following equations:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{V}(x) = \cosh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \sinh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{I}(x) = \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} sinh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{V_{r}} + \cosh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} x) \boldsymbol{I_{r}} }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\gamma} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{zy}} } is the propagation constant (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{-1}} )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{\frac{z}{y}}} } is the characteristic impedance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega} )
Note that the equations above are derived here.
By inspection, the ABCD parameters of the above equations can be represented in matrix form (for a line of length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l \, } metres) as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{s}} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{I_{s}} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \cosh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) & \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \sinh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) \\ \\ \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} sinh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) & \cosh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} \boldsymbol{V_{r}} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{I_{r}} \end{matrix} \right] \, }
Equivalent Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} Line
The "equivalent Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} " line model is essentially a line model with the same circuit structure as the nominal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} line (i.e. Figure 5), but the ABCD parameters of the distributed parameter line. In order to get the same ABCD parameters as the distributed parameter line, the nominal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} line impedance Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z}} and admittance Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y_{C} \,} need to be adjusted such that:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} A & C \\ B & D \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z'} \boldsymbol{Y'}}{2} \right) & \boldsymbol{Z'} \\ \\ \boldsymbol{Y'} \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z'} \boldsymbol{Y'}}{4} \right) & \left( 1 + \frac{\boldsymbol{Z'} \boldsymbol{Y'}}{2} \right) \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} \cosh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) & \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \sinh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) \\ \\ \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} sinh (\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) & \cosh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) \end{matrix} \right] \, }
Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z'}}
and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Y'} \,}
are the adjusted line impedance and admittance respectively (see conversion from nominal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi}
values below)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l \, } is the length of the line (m)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\gamma} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{zy}} } is the propagation constant (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{-1}} )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} = \sqrt{\boldsymbol{\frac{z}{y}}} } is the characteristic impedance (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega} )
The adjusted line parameters can be calculated from the nominal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} line parameters as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z'} = \left[ \frac{\sinh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l)}{\boldsymbol{\gamma} l} \right] \boldsymbol{Z} }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\boldsymbol{Y'}}{2} = \left[ \frac{\tanh \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{\gamma} l}{2} \right)}{\frac{\boldsymbol{\gamma} l}{2}} \right] \frac{\boldsymbol{Y}}{2} }
Alternatively, the adjusted line parameters can also be represented as follows:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{Z'} = \boldsymbol{Z}_{c} \sinh(\boldsymbol{\gamma} l) }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\boldsymbol{Y'}}{2} = \frac{1}{\boldsymbol{Z}_{c}} \tanh \left( \frac{\boldsymbol{\gamma} l}{2} \right) }
Click here for the full derivation of the calculation of the adjusted line parameters, including the alternative representation.